


Our Technologies
At Aperture Innovations, we use nature as an inspiration to structurally design and architect nanomaterials for applications in Health and the Environment. Nanomaterials possess unique physico-chemical features, including remarkable optical and catalytic properties.
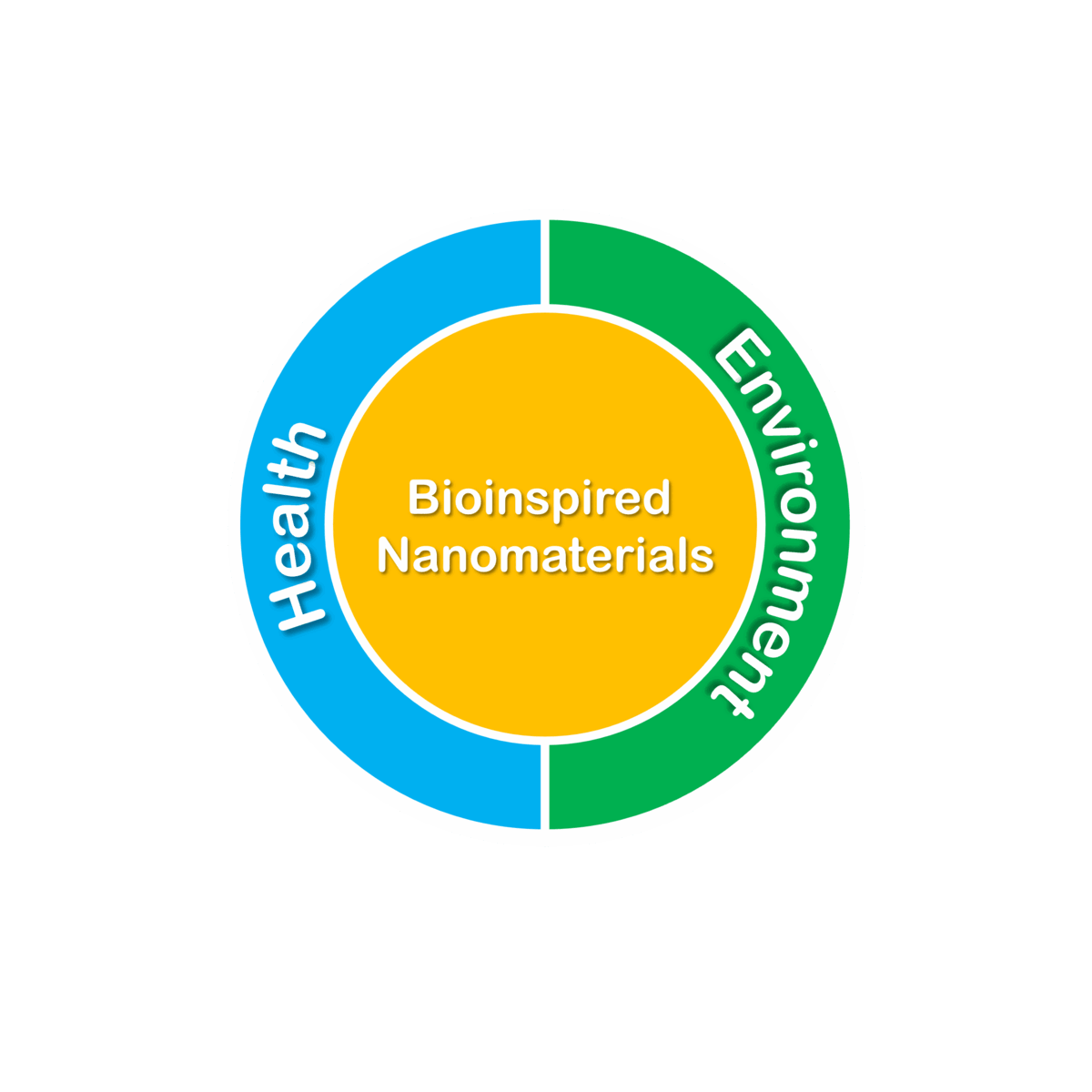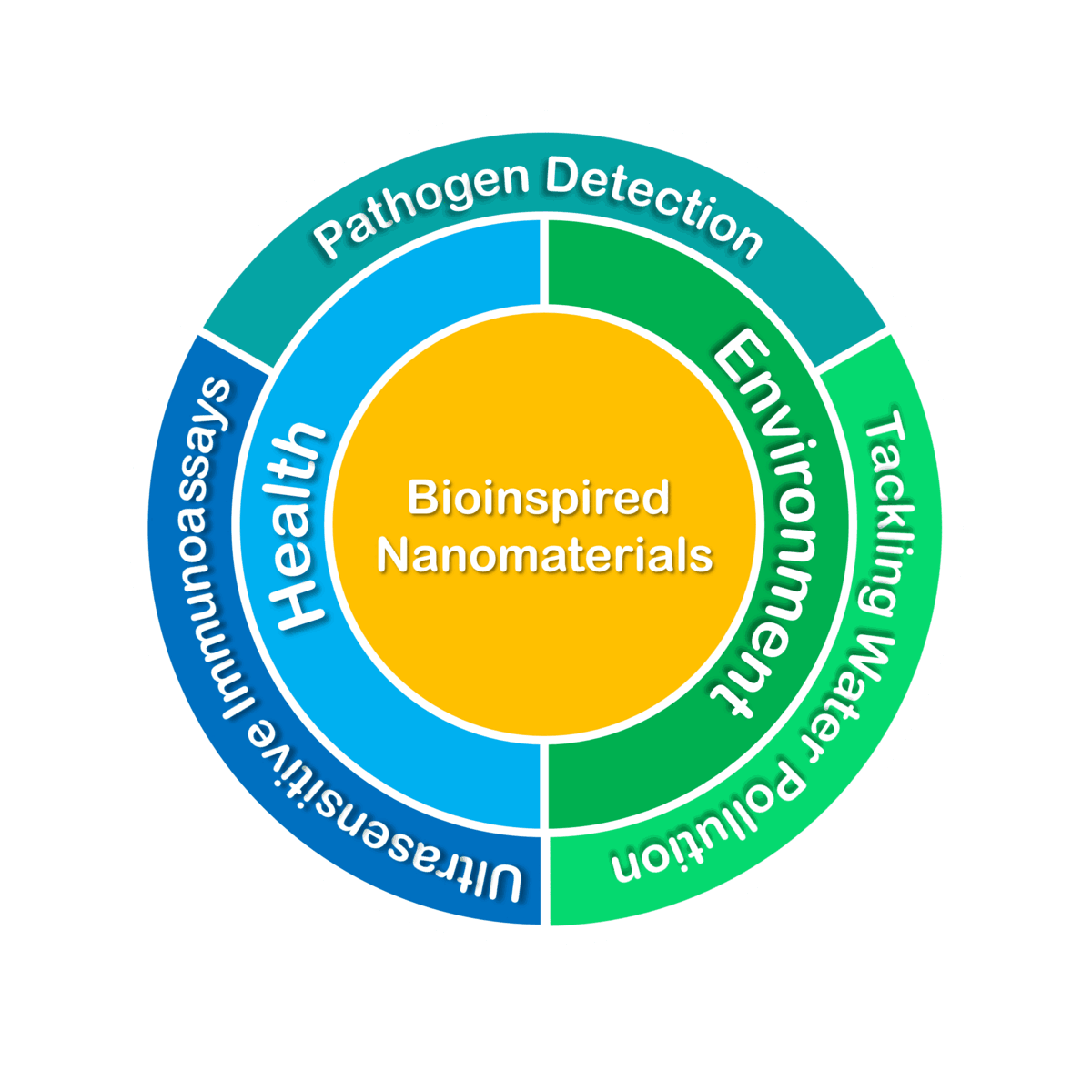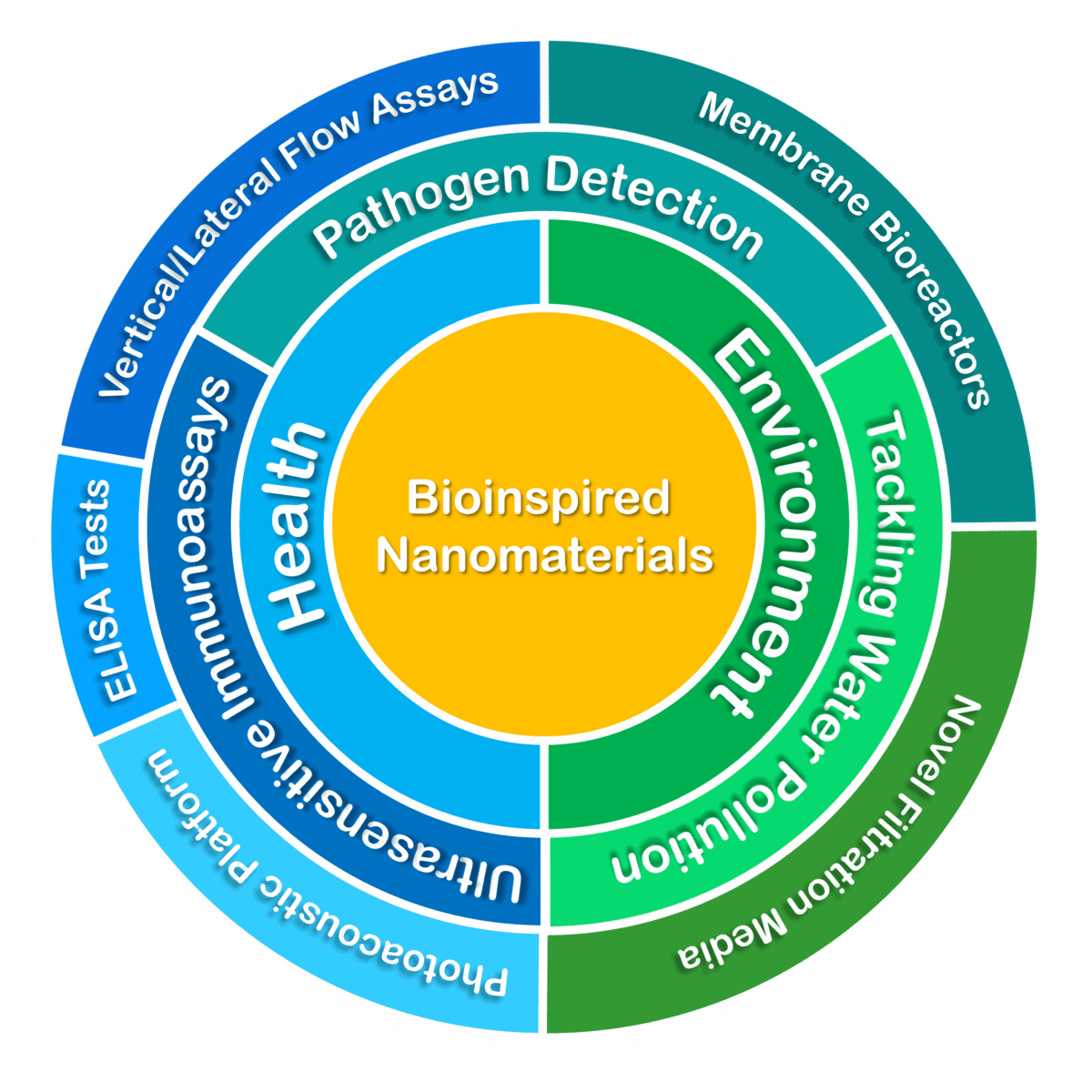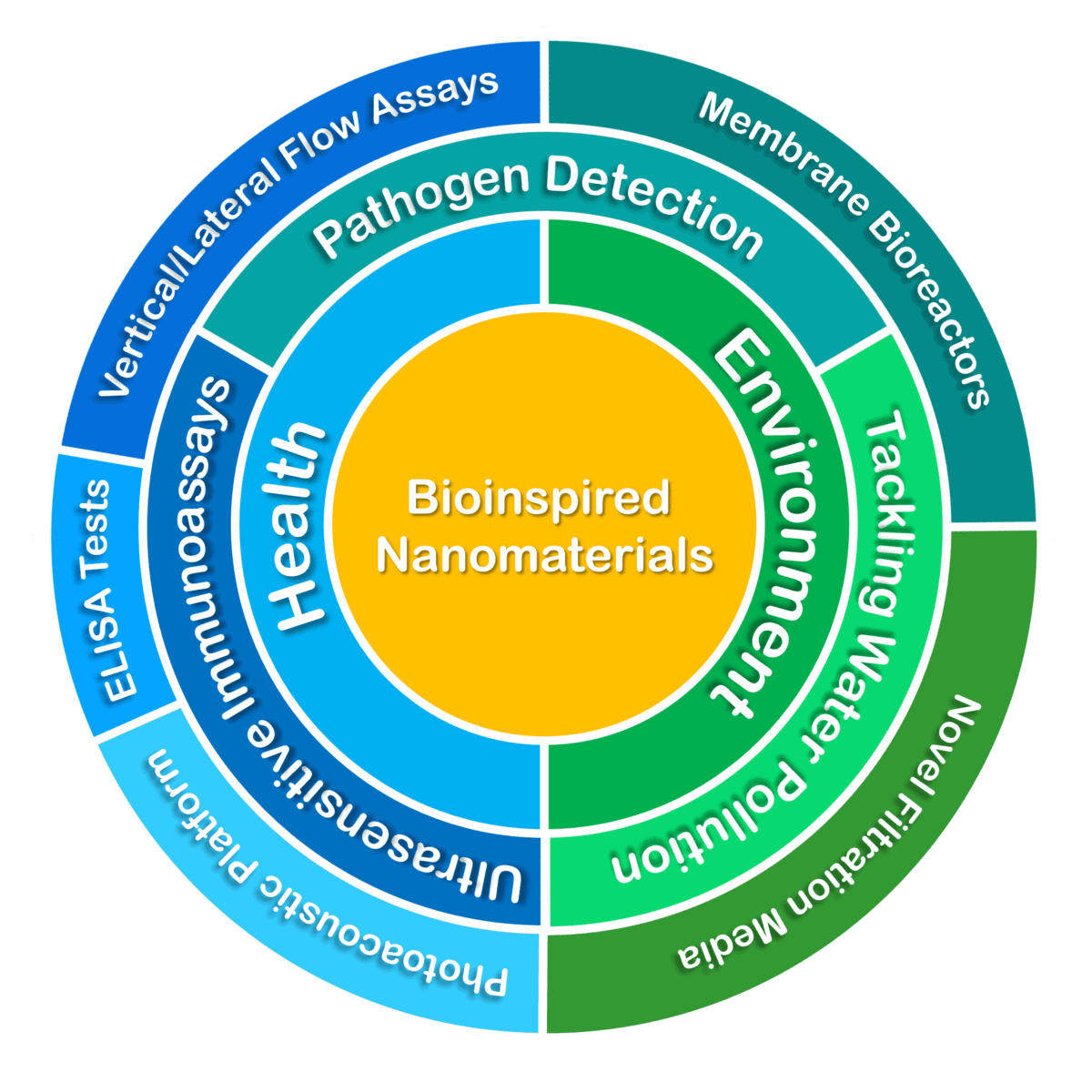
Our Target Market and Approach
Natural enzymes are highly effective biocatalysts, allowing chemical reactions to occur rapidly even under mild conditions, and more importantly, with high selectivity. The high efficiency and selectivity are immensely desirable properties for sensing and monitoring applications. However, natural enzymes, including proteins suffer from limitations such as low thermostability and narrow pH window, which will lead to denaturation and severely reduce their enzymatic activities. Low thermostability also places stringent requirements on the storage, transportation and handling of natural enzymes, which can be labour- and infrastructure-intensive for the users. Susceptible denaturation adds complexity to the interpretation of sensing and monitoring outputs, which may yield a false positive/negative outcome.
From this perspective, structurally designed nanomaterials address these limitations by offering high stability, while maintaining the desirable catalytic activities. By incorporating the unique physicochemical properties and enzyme-like activities, these nanoparticles exhibit promising applications in different fields such as the biomedical sector (in vitro diagnostics/and therapeutics) and the environmental sector (detection and remediation of inorganic and organic pollutants).
One example of bioinspiration is the ability for certain nanomaterials to mimic natural biological enzymes.
Technologies Under Development
Synthesis of Various Core-Shell Nano-Architectures Using Multi-Metallic Nanoparticles

One example of structural design is in the use of bi- and/or tri-metallic nanoparticles to form a core-shell structure with controllable features.
Interested in our core-shell multi-metallic nanoparticles? Please contact us here.
Development of Ultrasensitive Immunoassays (Colorimetric Approach)
Core-shell designed multi-metallic nanoparticles can be used as natural enzyme replacements, to catalyse the reaction of chromogenic ELISA substrates (such as TMB, ABTS, OPD and DAB). These nano-catalysts have a much wider thermal and chemical stability window, thus boosting the ability to re-use an ELISA plate for optimisation of protocols (i.e. raising the assay temperature, exposure to harsher chemical/pH), saving assay development time, labour costs and materials.


Oxidation of TMB (from colourless to blue-green) using a nano-catalyst and HRP.
Interested in using Aperture's nano-catalyst in your immunoassay? Please contact us here.
Pathogen Detection
We aim to develop a field-deployable rapid biosensing device to detect waterborne pathogens, with E. coli as the first targeted pathogen. The device will also be highly adaptable and customisable for the detection of other waterborne pathogens, such as low biosafety level (1 or 2) biological pathogens. The portability, rapid turnaround time and ease-of operation make it highly beneficial for first responders, which could aid in immediate risk assessment and mitigation of on-site emergencies arising from bioterrorism, biosecurity and contamination of drinking water.

Interested in using Aperture's pathogen detection platform? Please contact us here.
Tackling Water Pollution
Many toxic compounds including pesticides, pharmaceuticals, dyes, other organic and inorganic substances have been discharged into the environment causing significant damage to our ecological system. Significant efforts have been devoted to remediate these pollutants by removal or degradation to less harmful products. Natural enzymes possessing peroxidase and/or oxidase-like behaviour have been used to degrade organic pollutants. However, microbes and enzymes can only be functional and effective in narrow thermal and pH windows. The cost of producing enzymes, their lack of recyclability and the fact that biodegradation can be quite slow have hindered their large-scale, widespread application in environmental pollutant remediation. This creates an opportunity for bioinspired catalytic nanomaterials as alternatives for remediation. We are currently designing nanomaterials which possess remarkable oxidase-like behaviour to degrade pollutants through oxidative means.
.png)
Remazol
Blue Dye
Remazol Blue Dye
+ Nano-catalyst
+ H2O2

Decolourisation (via oxidation) of blue dye in the presence of Aperture's nano-catalyst
Interested in using Aperture's nano-catalyst in water remediation? Please contact us here.
Our Capabilities
Experts in:
-
Synthesis and characterisation of various metal nanoparticles
-
Surface functionalisation/modification of metal nanoparticles and carbon nanomaterials
-
Rational nano-architectural design of chemical and bio-sensing interaces
-
Development of optical, electrochemical and photoacoustic sensing platforms
Our Facilities
Our facilities at Lindfield, NSW are at the heart of Australia’s most dynamic physical and chemical science campus as well as a driver of multidisciplinary research. Our facilities and expertise in the synthesis and characterisation of nanomaterials sit alongside those in biosciences, engineering, medicine, and environmental sciences.
Learn more about our facilities here.